Certification
Upon fulfilling the course requirements with a minimum attendance rate of 100% and demonstrating proficiency in the assessments, candidates will be awarded a
- Certificate of Completion from AAT Training Hub
We are an accredited training provider for the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (International- CBTA).
IATA mandates that all personnel involve in handling storage, loading and preparation of Dangerous Goods by Air Transport must attend a training program as per the latest IATA DGR Manual.
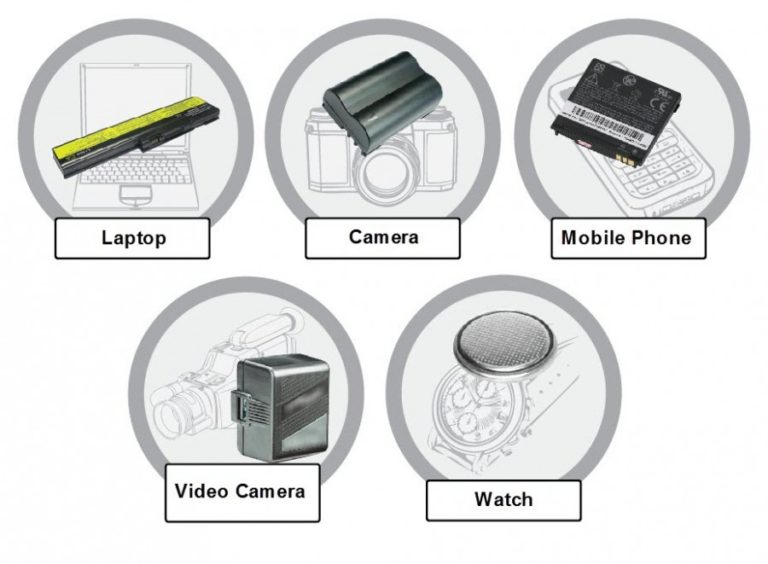
This course is aimed at key personal working with lithium batteries in
the air industry who are engaged in defining quality and safety
management systems around the air transport and handling of lithium
batteries.
Manufacturers of lithium batteries and shippers of lithium batteries by air transport will benefit from the knowledge gained from this course, where our expert DGR trainer will guide learners through the packaging requirements as per the latest IATA requirements.
Able to read and write in English
Duration: 9 hours
Language: English
Validity: 24 months
Locations:



Upon fulfilling the course requirements with a minimum attendance rate of 100% and demonstrating proficiency in the assessments, candidates will be awarded a
Manufacturers of lithium batteries and shippers of lithium batteries by air transport will benefit from the knowledge gained from this course, where our expert DGR trainer will guide learners through the packaging requirements as per the latest IATA requirements.
Upon successful completion of the course, you will receive
You can: